Learn AI Agents Definition: A Simple Guide to Digital Assistants You Need in 2026
Understanding AI Agents in Today’s Digital Landscape
Imagine having a tireless assistant who never sleeps, learns from every interaction, and can handle multiple tasks simultaneously without breaking a sweat. This isn’t science fiction anymore—it’s the reality of AI agents.
The AI agents definition has evolved significantly over the past few years. These intelligent software programs are revolutionizing how businesses operate and how we interact with technology daily. From customer service chatbots to sophisticated automation systems, AI agents are becoming indispensable tools in our digital ecosystem.
As artificial intelligence continues to advance at breakneck speed, understanding what AI agents are and how they function has become crucial for businesses and individuals alike. Whether you’re a business owner looking to streamline operations or simply curious about the technology shaping our future, this guide will demystify AI agents and show you their practical applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fundamental definition of AI agents, examine their key benefits, walk through implementation strategies, and address common challenges you might encounter along the way.
What Exactly Are AI Agents? Breaking Down the Definition
At its core, the AI agents definition refers to autonomous software programs that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals without constant human intervention. Think of them as digital workers with the ability to learn, adapt, and improve over time.
The Core Components of AI Agents
AI agents operate through several essential components that work together seamlessly. First, they have sensors or input mechanisms that allow them to gather information from their environment. This could be text input from users, data from databases, or real-time information from various sources.
Second, they possess decision-making capabilities powered by machine learning algorithms and natural language processing. These technologies enable AI agents to analyze information, understand context, and determine the best course of action.
Third, they have actuators or output mechanisms that allow them to execute actions, whether that’s responding to a customer query, triggering a workflow, or updating a database.
Types of AI Agents in Modern Applications
The landscape of AI agents is diverse and constantly expanding. Simple reflex agents respond to specific conditions with predetermined actions, much like a thermostat adjusting temperature. Model-based agents maintain an internal understanding of their environment, allowing for more sophisticated decision-making.
Goal-based agents work toward specific objectives, evaluating different paths to achieve desired outcomes. Utility-based agents go further by weighing multiple factors to make optimal decisions. Learning agents represent the most advanced category, continuously improving their performance through experience and feedback.
Current Trends and Market Growth
The AI agent market is experiencing explosive growth. According to recent industry reports, the global AI market is projected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2030, with AI agents playing a significant role in this expansion. Businesses across industries are investing heavily in AI agent technology, with 72% of enterprises planning to increase their AI budgets in 2025.
The rise of generative AI has particularly accelerated AI agent adoption, enabling more natural conversations and creative problem-solving capabilities that were previously impossible.
The Powerful Benefits of Implementing AI Agents
Understanding the AI agents definition is just the beginning. The real value lies in recognizing how these digital assistants can transform your operations and deliver measurable results.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
AI agents excel at handling repetitive, time-consuming tasks that typically drain human resources. By automating routine processes, businesses can reduce operational costs by up to 40% while simultaneously improving accuracy and speed.
Consider customer service operations. AI agents can handle thousands of inquiries simultaneously, providing instant responses 24/7 without fatigue. This means faster resolution times, happier customers, and significant savings on staffing costs.
They also eliminate human error in data entry, processing, and analysis tasks, ensuring consistency and reliability across operations.
Scalability Without Proportional Resource Investment
One of the most compelling advantages of AI agents is their ability to scale effortlessly. As your business grows, AI agents can handle increased workload without requiring proportional increases in resources or infrastructure.
During peak periods or unexpected surges in demand, AI agents maintain consistent performance levels. This scalability ensures you never miss opportunities or disappoint customers due to capacity constraints.
Improved Decision-Making Through Data Analysis
AI agents process vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and insights that humans might miss. They can analyze customer behavior, market trends, and operational metrics to provide actionable recommendations.
Enhanced Customer Experience and Personalization
Modern consumers expect personalized, immediate service. AI agents deliver exactly that by remembering customer preferences, anticipating needs, and providing tailored recommendations.
They create seamless experiences across multiple channels, ensuring consistency whether customers interact via chat, email, or voice. This level of personalization drives customer satisfaction scores up by an average of 33% according to recent studies.
How to Successfully Implement AI Agents in Your Organization
Now that you understand the AI agents definition and their benefits, let’s explore the practical steps for implementation.
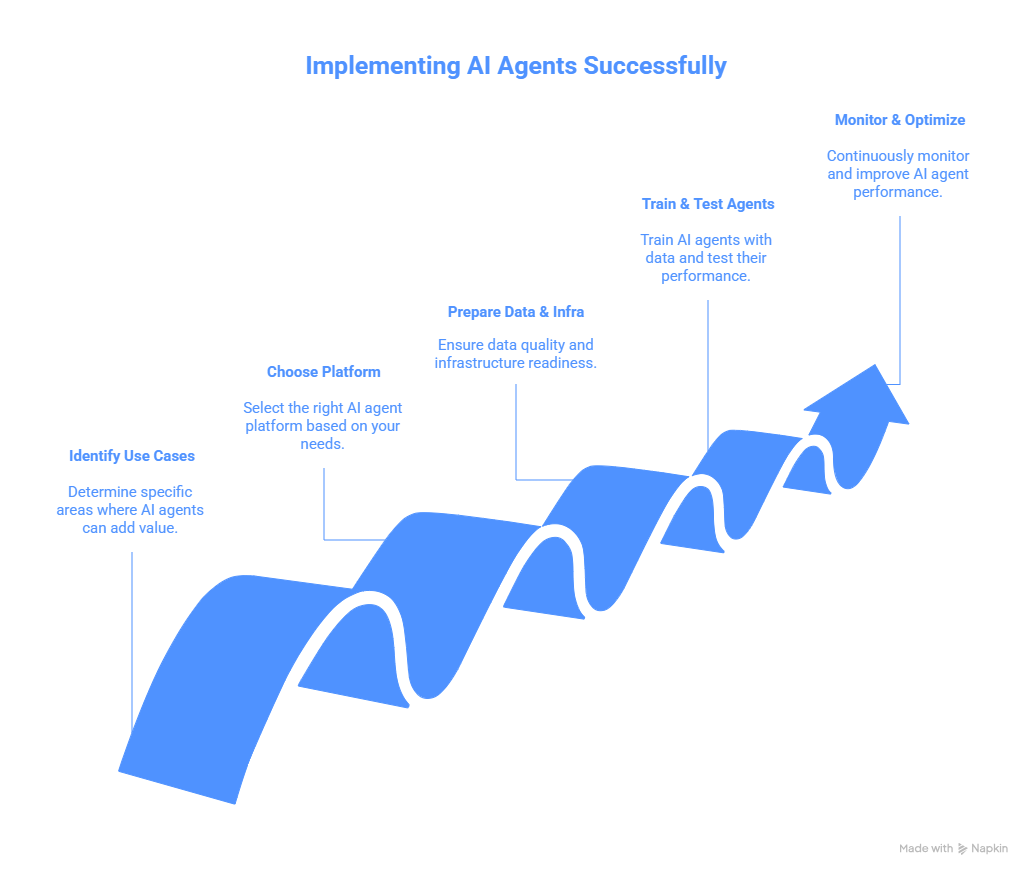
Step 1: Identify Your Use Cases and Objectives
Begin by mapping out specific processes or challenges where AI agents could add value. Look for tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, or require processing large amounts of information quickly.
Common starting points include customer support automation, lead qualification, appointment scheduling, data entry, and basic troubleshooting. Define clear success metrics for each use case, such as response time reduction, cost savings, or customer satisfaction improvements.
Prioritize use cases based on potential impact and implementation complexity. Starting with quick wins builds momentum and demonstrates value to stakeholders.
Step 2: Choose the Right AI Agent Platform
The market offers numerous AI agent platforms, each with different capabilities and specializations. Evaluate options based on your specific requirements, technical infrastructure, and budget constraints.
Consider factors like integration capabilities with existing systems, customization options, scalability, security features, and vendor support. Popular platforms include conversational AI solutions, robotic process automation tools, and specialized industry-specific agents.
Request demos and pilot programs to test functionality before committing to large-scale implementation.
Step 3: Prepare Your Data and Infrastructure
AI agents require quality data to function effectively. Audit your existing data sources, ensuring they’re clean, organized, and accessible. Establish data governance policies to maintain quality over time.
Assess your technical infrastructure to ensure it can support AI agent deployment. This includes evaluating computing resources, network capabilities, and security protocols.
Create integration points between the AI agent platform and your existing systems, such as CRM software, databases, and communication channels.
Step 4: Train and Test Your AI Agents
Training is crucial for AI agent success. Feed your agents with relevant data, common scenarios, and desired responses. Use historical interactions to teach them appropriate behavior and decision-making patterns.
Conduct thorough testing in controlled environments before full deployment. Test edge cases, unusual scenarios, and potential failure points. Gather feedback from test users and refine agent responses accordingly.
Implement a phased rollout approach, starting with limited deployment and gradually expanding as confidence grows.
Step 5: Monitor, Optimize, and Scale
Post-deployment monitoring is essential for long-term success. Track key performance indicators like accuracy rates, user satisfaction, task completion times, and error frequencies.
Establish feedback loops that allow continuous learning and improvement. Regularly review agent interactions to identify areas for enhancement.
As your AI agents prove their value, expand their responsibilities and deploy them across additional use cases. Document lessons learned to streamline future implementations.
Overcoming Common Challenges with AI Agents
While AI agents offer tremendous benefits, implementation isn’t without challenges. Understanding these obstacles and their solutions ensures smoother adoption.
Managing User Expectations and Trust
Many users approach AI agents with skepticism or unrealistic expectations. Some expect human-level understanding in all situations, while others distrust automated systems entirely.
Address this by being transparent about AI agent capabilities and limitations. Clearly communicate when users are interacting with an AI agent versus a human. Provide easy escalation paths to human support when needed.
Build trust gradually by ensuring consistent, accurate performance. Share success stories and demonstrate value through measurable improvements.
Handling Complex or Ambiguous Situations
AI agents sometimes struggle with nuanced situations, sarcasm, or highly complex queries that require deep contextual understanding. This limitation can frustrate users and damage credibility.
Implement robust fallback mechanisms that recognize when situations exceed agent capabilities. Design smooth handoff processes to human experts for complex cases.
Continuously expand your AI agent’s knowledge base and training data to handle increasingly sophisticated scenarios. Use machine learning to help agents learn from challenging interactions.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many organizations operate with older technology systems that weren’t designed for AI integration. This creates technical barriers to AI agent implementation.
Work with experienced integration specialists who understand both modern AI platforms and legacy systems. Consider middleware solutions that bridge the gap between old and new technologies.
In some cases, gradual system modernization alongside AI agent deployment provides the best long-term solution.
Maintaining Data Privacy and Security
AI agents often handle sensitive information, raising concerns about data privacy and security breaches. Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity.
Implement robust security measures including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Ensure your AI agent solution complies with relevant regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or industry-specific requirements.
Establish clear data handling policies and train your team on privacy best practices. Choose vendors with strong security track records and transparent data practices.
Embracing the Future with AI Agents
The AI agents definition encompasses far more than simple automation—these intelligent digital assistants represent a fundamental shift in how we work, serve customers, and solve problems. From enhancing operational efficiency to delivering personalized customer experiences, AI agents are proving their value across industries and applications.
As we’ve explored, successful AI agent implementation requires careful planning, the right technology choices, and ongoing optimization. While challenges exist, the solutions are well-established and manageable with proper preparation and expertise.
The organizations that embrace AI agents today position themselves for competitive advantage tomorrow. These digital assistants free human workers to focus on creative, strategic, and relationship-building activities that truly require human intelligence and empathy.
Whether you’re just beginning to explore AI agents or ready to expand your existing implementation, the key is taking that first step. Start small, measure results, learn continuously, and scale what works.
Ready to harness the power of AI agents for your organization? The Crunch specializes in helping businesses successfully implement AI solutions that deliver real results. Our team of experts will guide you through every step of the journey, from strategy development to deployment and optimization.
Contact The Crunch today to schedule your free consultation and discover how AI agents can transform your business operations. Visit https://thecrunch.io/get-a-proposal/ to get started.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is an AI agent?
2. How do AI agents work?
3. What are the main types of AI agents?
4. How are AI agents different from traditional software programs?
5. What are the benefits of using AI agents?
6. Are AI agents expensive to implement?
7. What are common concerns about AI agents?
8. How can I get started with AI agents?
9. Can AI agents learn and improve over time?
10. What industries use AI agents?
11. Do I need programming skills to use AI agents?
12. Are AI agents safe to use?