7 Types of Transformative AI Agents for Business That Will Transform Your Operational Efficiency
Introduction: The AI Revolution in Modern Business
Imagine having a team of tireless employees who work 24/7, never take breaks, and continuously improve their performance. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the reality of AI agents for business in 2025.
Business leaders worldwide are grappling with mounting operational costs, talent shortages, and the relentless pressure to do more with less. Traditional automation has reached its limits, leaving companies searching for the next breakthrough. Enter AI agents: intelligent software systems that don’t just follow rules but learn, adapt, and make decisions autonomously.
These sophisticated digital workers are revolutionizing everything from customer service to financial analysis, delivering ROI that often exceeds 300% within the first year. Whether you’re running a startup or managing an enterprise, AI agents for business represent the most significant operational transformation since the internet.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore seven game-changing AI agents that are reshaping business operations, how to implement them effectively, and the tangible benefits they deliver. You’ll discover practical strategies to integrate these technologies into your workflow and overcome common implementation challenges.
Understanding AI Agents for Business: What They Are and Why They Matter
AI agents are autonomous software programs powered by artificial intelligence that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals without constant human supervision. Unlike traditional automation tools that follow rigid if-then rules, AI agents for business leverage machine learning, natural language processing, and advanced algorithms to handle complex, nuanced tasks.
According to McKinsey’s 2024 research, companies implementing AI agents report an average productivity increase of 40% in automated departments. Gartner predicts that by 2026, over 80% of enterprises will have deployed AI agents in some capacity, up from just 15% in 2023.
What makes AI agents particularly valuable is their ability to handle ambiguity. They can interpret unstructured data, understand context, learn from interactions, and improve over time. This adaptability makes them ideal for dynamic business environments where conditions constantly change.
The Evolution from Automation to Intelligence
Traditional automation excels at repetitive, rule-based tasks. AI agents go several steps further by incorporating cognitive capabilities. They can understand natural language, recognize patterns in data, predict outcomes, and even engage in creative problem-solving.
For instance, while a basic chatbot might answer FAQs using keyword matching, an AI agent can understand customer intent, access multiple systems to gather information, resolve complex issues, and learn from each interaction to improve future responses.
Key Characteristics of Effective Business AI Agents
The most impactful AI agents for business share several critical attributes:
- Autonomy: They operate independently within defined parameters, requiring minimal human intervention
- Learning capability: They improve performance through experience and feedback
- Goal-oriented behavior: They work toward specific business objectives rather than just executing tasks
- Contextual awareness: They understand the broader business context and adapt accordingly
- Integration capability: They seamlessly connect with existing business systems and workflows
7 Transformative AI Agents for Business Operations
1. Customer Service AI Agents
Customer service AI agents have evolved far beyond simple chatbots. Modern solutions like Intercom’s Fin and Zendesk’s AI agents handle up to 70% of customer inquiries without human intervention. They understand complex questions, access customer history across multiple touchpoints, and provide personalized solutions.
These agents reduce response times from hours to seconds, operate across multiple channels simultaneously, and maintain consistent service quality regardless of volume. Companies like Shopify report 25% cost reductions in support operations while simultaneously improving customer satisfaction scores by 15-20%.
2. Sales and Lead Qualification Agents
Sales AI agents revolutionize how businesses identify, nurture, and convert prospects. Tools like Drift’s conversational AI and Salesforce’s Einstein engage website visitors in real-time, qualify leads based on behavioral signals and firmographic data, and route high-value prospects to human sales representatives at the optimal moment.
These agents analyze thousands of data points to score leads accurately, personalize outreach at scale, and predict which prospects are most likely to convert. B2B companies using sales AI agents report 50% increases in qualified leads and 35% shorter sales cycles.
3. Financial Analysis and Forecasting Agents
Financial AI agents transform raw data into actionable insights. They continuously monitor financial metrics, identify anomalies, predict cash flow challenges, and recommend optimization strategies. Unlike human analysts who might review reports weekly or monthly, these agents work in real-time.
Companies like BlackLine and Sage have integrated AI agents that automate reconciliation processes, detect fraud patterns, and generate forecasts with 90%+ accuracy. CFOs using these tools report saving 15-20 hours weekly on routine analysis while making more informed strategic decisions.
4. Human Resources and Recruitment Agents
HR AI agents streamline talent acquisition and employee management. They screen resumes, conduct initial candidate assessments, schedule interviews, answer employee questions about benefits and policies, and even predict employee turnover risk.
Platforms like HireVue and Eightfold AI use agents that eliminate unconscious bias in hiring, reduce time-to-hire by 40%, and improve candidate quality. For employee management, agents handle routine HR inquiries, freeing human HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives and complex employee relations.
5. Marketing Campaign Optimization Agents
Marketing AI agents for business continuously test, learn, and optimize campaigns across channels. They analyze audience behavior, adjust targeting parameters, optimize ad spend allocation, personalize content, and predict campaign performance before launch.
Tools like Persado and Albert AI have demonstrated the ability to improve conversion rates by 30-50% while reducing customer acquisition costs. These agents process millions of data points to identify which messages resonate with specific audience segments and automatically adjust campaigns in real-time.
6. Supply Chain and Inventory Management Agents
Supply chain AI agents predict demand fluctuations, optimize inventory levels, identify potential disruptions, and recommend procurement strategies. They analyze historical data, market trends, weather patterns, and geopolitical factors to make sophisticated forecasting decisions.
Retailers using inventory management agents from companies like Blue Yonder report 20-30% reductions in excess inventory while simultaneously decreasing stockouts by 50%. These agents ensure products are in the right place at the right time without tying up excessive capital in inventory.
7. Cybersecurity and Threat Detection Agents
Security AI agents monitor networks 24/7, identifying threats that human analysts might miss. They detect unusual patterns, respond to incidents in milliseconds, and learn from each attack attempt to strengthen defenses.
Solutions like Darktrace and CrowdStrike use AI agents that identify zero-day threats, contain breaches automatically, and reduce incident response times from hours to minutes. Organizations report 60% reductions in successful attacks and 80% faster threat remediation.
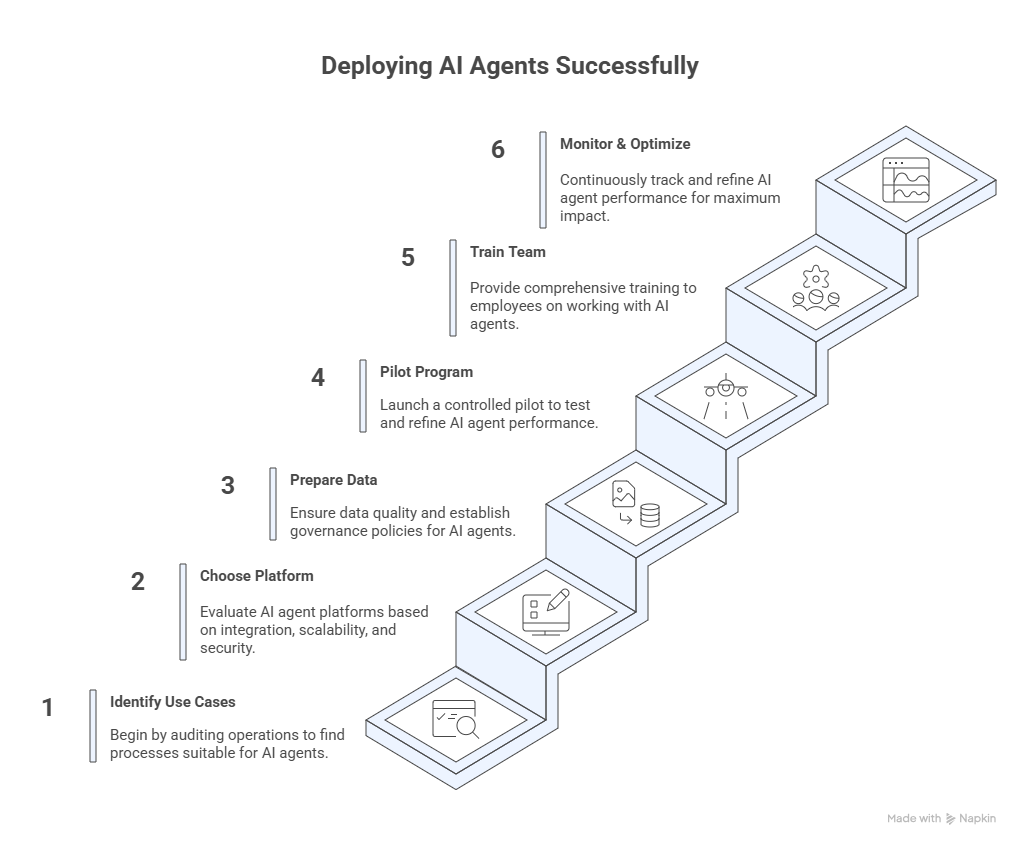
Implementation Guide: Deploying AI Agents Successfully
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Use Cases
Begin by auditing your operations to identify processes that are repetitive, data-intensive, time-consuming, or prone to human error. The best initial candidates for AI agents for business are tasks that meet multiple criteria: high volume, clear success metrics, and significant business impact.
Conduct stakeholder interviews across departments to understand pain points. Look for processes where employees spend significant time on routine tasks rather than strategic work. Create a prioritization matrix based on implementation complexity versus potential ROI.
Step 2: Choose the Right AI Agent Platform
Not all AI agent solutions are created equal. Evaluate platforms based on integration capabilities with your existing tech stack, scalability to handle growth, customization options for your specific needs, security and compliance features, and vendor support quality.
Request demos and pilot programs before committing. Test agents with real business scenarios to assess performance. Consider both specialized point solutions for specific functions and comprehensive platforms that offer multiple agent types.
Step 3: Prepare Your Data Infrastructure
AI agents are only as effective as the data they access. Audit your data quality, ensuring accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Establish data governance policies that define access rights, usage guidelines, and privacy protections.
Integrate data sources so agents can access information across systems. Clean historical data to remove duplicates, errors, and inconsistencies. Create data pipelines that feed agents with real-time information.
Step 4: Start with a Pilot Program
Launch your first AI agent in a controlled environment with limited scope. Choose a non-critical process initially to minimize risk while learning. Define clear success metrics before deployment, such as time saved, error reduction, or cost savings.
Monitor performance closely during the pilot phase. Gather feedback from users who interact with the agent. Document lessons learned and adjust your approach before scaling.
Step 5: Train Your Team
Successful AI agent implementation requires human adaptation. Provide comprehensive training on how to work alongside AI agents, when to intervene, and how to provide feedback that improves agent performance.
Address concerns about job displacement proactively. Emphasize that AI agents for business handle routine tasks, freeing employees for higher-value work that requires human creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking. Involve employees in the implementation process to build buy-in.
Step 6: Monitor, Measure, and Optimize
Establish dashboards that track agent performance against KPIs. Monitor accuracy rates, processing times, user satisfaction, and business impact. Set up alerts for anomalies or performance degradation.
Continuously refine agent behavior based on performance data. AI agents improve through feedback loops—the more you monitor and adjust, the better they become. Schedule regular reviews to assess ROI and identify expansion opportunities.
Overcoming Common Challenges with AI Agents for Business
Challenge 1: Integration Complexity
Many businesses struggle to connect AI agents with legacy systems. These older platforms often lack modern APIs or use proprietary data formats that don’t communicate easily with AI tools.
Solution: Invest in middleware platforms that bridge legacy systems and modern AI agents. Consider API development to expose necessary data and functions. In some cases, gradual system modernization may be necessary. Partner with integration specialists who understand both your existing infrastructure and AI technologies.
Challenge 2: Data Quality and Availability
AI agents require clean, comprehensive data to function effectively. Organizations often discover their data is siloed, inconsistent, or incomplete when attempting to deploy agents.
Solution: Implement a data quality initiative before deploying AI agents. Establish data governance frameworks that ensure ongoing quality. Use data cleaning tools to standardize formats and remove errors. Create centralized data repositories that agents can access reliably.
Challenge 3: Employee Resistance
Workers may fear that AI agents for business will replace their jobs, leading to resistance and sabotage of implementation efforts.
Solution: Communicate transparently about how AI agents will change roles rather than eliminate them. Involve employees in selecting and configuring agents. Highlight how automation of routine tasks enables more interesting, strategic work. Provide retraining opportunities for employees whose roles evolve significantly.
Challenge 4: Security and Compliance Concerns
AI agents that access sensitive data or make autonomous decisions raise legitimate security and regulatory concerns, particularly in industries like healthcare, finance, and legal services.
Solution: Choose AI agent platforms with robust security features including encryption, access controls, and audit trails. Implement human-in-the-loop processes for high-stakes decisions. Work with legal and compliance teams to ensure agents operate within regulatory boundaries. Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
Challenge 5: Measuring ROI
Quantifying the business impact of AI agents can be challenging, especially for benefits like improved decision quality or employee satisfaction.
Solution: Establish baseline metrics before implementation. Track both quantitative measures like time saved and cost reduction, and qualitative factors like employee satisfaction and customer experience. Use A/B testing where possible to isolate the agent’s impact. Calculate total cost of ownership including implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance.
Conclusion: Embracing the AI Agent Revolution
AI agents for business represent more than just another technology trend—they’re a fundamental shift in how work gets done. From customer service to financial analysis, these intelligent systems are delivering measurable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and scalability.
The seven AI agents we’ve explored—customer service, sales qualification, financial analysis, HR and recruitment, marketing optimization, supply chain management, and cybersecurity—address critical business functions across industries. Companies that implement these technologies strategically are gaining significant competitive advantages through reduced costs, faster operations, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Success with AI agents requires thoughtful planning, quality data infrastructure, employee engagement, and continuous optimization. Start with high-impact use cases, pilot thoroughly, and scale based on proven results. Address integration challenges proactively and maintain focus on business outcomes rather than technology for its own sake.
The businesses that thrive in the coming years will be those that effectively combine human creativity and strategic thinking with AI agent capabilities for routine tasks and data processing. This partnership between human and artificial intelligence creates organizations that are more agile, efficient, and innovative than either could be alone.
The question isn’t whether to adopt AI agents for business—it’s how quickly you can implement them effectively to stay competitive in an increasingly automated world.
Ready to transform your business operations with AI agents? The Crunch specializes in helping companies identify, implement, and optimize AI solutions tailored to their unique needs. Our team of experts will assess your operations, recommend the right AI agents, and guide you through successful deployment. Schedule your free consultation today and discover how AI agents can revolutionize your business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are AI agents for business?
2. How do AI agents work in a business setting?
3. What are the main benefits of using AI agents in business?
4. How do AI agents compare to traditional automation tools?
5. What types of tasks can AI agents automate in a business?
6. Are AI agents expensive to implement for small businesses?
7. What are common concerns about using AI agents in business?
8. How can a business get started with AI agents?
9. Do AI agents require technical expertise to manage?
10. Can AI agents integrate with existing business software?
11. How secure are AI agents for handling sensitive business data?
12. What industries can benefit most from AI agents?